Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
What is it?
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a nerve condition that can result in numbness, tingling, and weakness in the hand. It is a the most common cause of numbness in the hand.
What causes it?
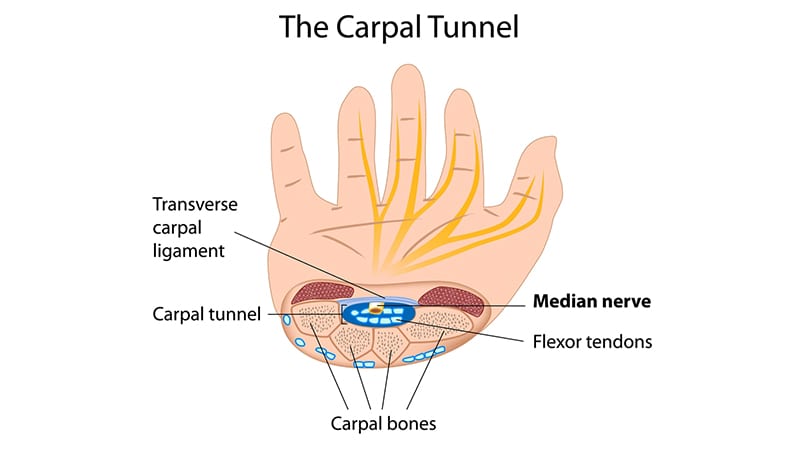
Pressure on a nerve called the median nerve at the level of the wrist causes carpal tunnel syndrome. The carpal tunnel is a space within the wrist through which tendons and the median nerve pass. The transverse carpal ligament forms the roof of the tunnel, and the bones of the wrist form the floor of the canal. Because of its enclosed nature, pressure can be generated on the nerve. This pressure causes dysfunction of the nerve that results in symptoms.
Symptoms:
Carpal tunnel syndrome usually results in numbness and tingling in the distribution of the median nerve. This includes the thumb, index finger, middle finger, and half of the ring finger. With mild cases, these symptoms are intermittent and can be activity or position dependent. Many people report symptoms with activities such as driving, riding a motorcycle, writing, or other heavy use of the hands. Symptoms at night are also very common. Many patients report weakness or dropping of objects. Once the condition worsens, the symptoms increase in intensity and frequency. The numbness can become constant, and the muscles of the thumb innervated by the nerve may begin to weaken.
Diagnosis:
A good clinical history and physical examination is usually sufficient to arrive at a diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome. Special tests called nerve conduction studies and an electromyography can provide information on how well the median nerve is functioning, and whether the muscles are affected. These studies can support a diagnosis of carpal tunnel, and can also evaluate for other potential problems with nerve function.
Treatment:
Conservative treatment for carpal tunnel syndrome is often successful at improving symptoms and delaying or eliminating the need for surgery. Conservative treatment is usually undertaken for 6 months. In patients who are determined to have failed conservative management or who present with CTS in an advanced stage, surgery is indicated. The surgery to treat CTS is a release of the transverse carpal ligament. This is traditionally accomplished via an incision through the palm, or as an endoscopic procedure. In the endoscopic procedure, a smaller incision in the wrist allows placement of a camera and blade into the carpal tunnel, and the ligament is released from the inside. Both procedures adequately decompress the carpal tunnel.
Are you ready to get treated? Book your appointment here.

