Elbow Arthritis
What is it?
Elbow arthritis typically refers to the breakdown of the normal cartilage surfaces lining the elbow joint.
What causes it?
It can occur via many processes. Trauma, wear and tear of the joints over time, and systemic conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis can all result in elbow arthritis.
What are the symptoms?
The result of these processes is the development of pain in the elbow, made worse with range of motion, inflammation, stiffness of the elbow, and mechanical symptoms of catching or locking.
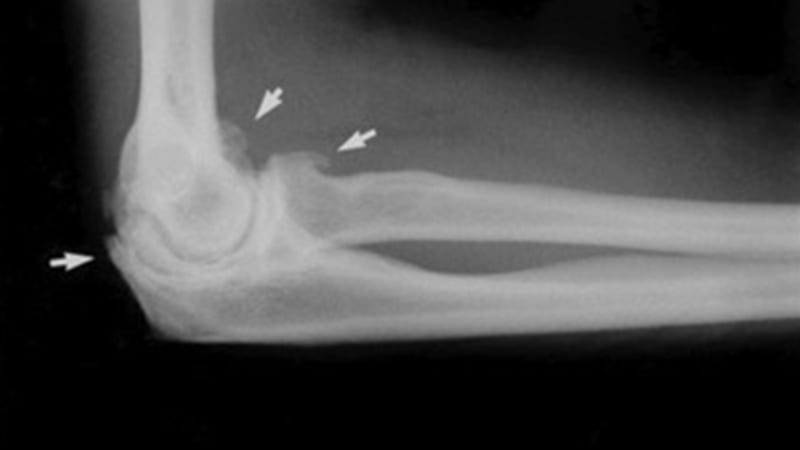
How is it diagnosed?
A history and physical examination is helpful to determine the cause of the arthritis and its effect on the patient. Xrays are the initial diagnostic study of choice. They are useful to show the severity of the arthritis, the location of the arthritis within the elbow, the presence of bone spurs or loose bodies within the elbow, the overall alignment of the elbow, and the presence of any hardware in the elbow. A CT scan can give a better three-dimensional map of the elbow, helpful for surgical planning.
How is it treated?
Conservative treatment of elbow arthritis can involve oral anti-inflammatory medication, splinting, therapy, and steroid injections. When conservative management fails, surgical debridement of bone spurs and loose bodies resulting from arthritis, combined with a capsular release, can decrease pain and improve range of motion. This can be accomplished through open incisions about the elbow, or in minimally invasive fashion using elbow arthroscopy. In this procedure a camera inserted into the joint provides visualization, while additional incisions allow for the insertion of working instruments. Some patients with severe arthritis, and others such as elderly patients with severe fractures, may be candidates for elbow joint replacement surgery.
Are you ready to get treated? Book your appointment here.

